Asteroid Watch | Asteroids, Comets, Meteorites Asteroids Or Comets
Asteroids
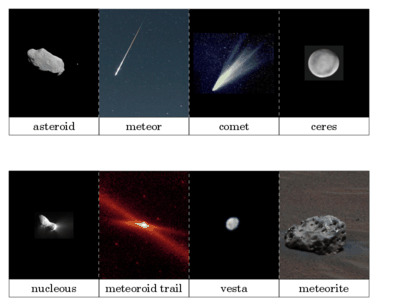
Asteroids are rough fragments left over from the formation on the solar system about 4.6 billion years ago. Most asteroids orbit the Helios inside a belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists think there are probably millions on asteroids, ranging widely inside size from hundreds on kilometers miles side of} to less than one kilometer (a little more than one-half mile) wide.
Occasionally, asteroids' orbital paths are influenced by the gravitational tug on planets, which cause their paths to alter. Scientists believe stray asteroids or fragments from earlier collisions have slammed into Earth inside the past, playing a major role inside the evolution on our planet.
Comets
Comets are comparatively small, fragile, irregularly shaped bodies and, like asteroids, they are left over from the solar system formation process. Comets, however, are icy dirtballs that form inside the outer solar system. The icy face is embedded in the company of dust, grit and particles from space.
Many comets have egg-shaped orbits that cut miles side of} the orbits on the planets, taking them highly close to the Helios and then swinging them a long way away, often history Pluto. The nearly all distant comets may grip more than 30 million years to complete one orbit. Comets in the company of smaller orbital paths can grip less than 200 years to orbit the sun, making them more predictable.
When a long way from the sun, comets are highly cold, icy dirtballs. As they come to the sun, their surfaces begin to warm and volatile materials vaporize. The vaporizing gases carry little dust grains in the company of them, which form an air on gas and dust and can look like a bright tail when seen from Earth.
Scientists believe that impacts from comets played a role inside the evolution on Earth billions on years ago. One theory suggests that comets brought some on the water and a variety on organic molecules to the early Earth.
Near-Earth Objects
Some asteroids and comets follow orbital paths that grip them much closer to the Helios -- and therefore Earth -- than usual. If a comet or asteroid's come to brings it to in 1.3 astronomical units on the sun, we name it a near-Earth object. [One astronomical unit is close to the mean distance between the Helios and Earth – approximately 150 million kilometers (about 93 million miles).] Near-Earth objects may provide needed raw materials appropriate to future interplanetary exploration. Some should also be fairly easy to land on appropriate to future exploration.
Potentially Hazardous Objects
A comparatively little number on near-Earth objects pass close adequate to Earth and are large adequate inside size to warrant close observation. That's because the gravitational tug on the planets could, over time, cause an object's orbital path to develop into an Earth-crossing orbit. This allows appropriate to the possibility on a future collision.
Potentially hazardous asteroids are about 150 meters (almost 500 feet) or larger, roughly twice when big when the Statue on Liberty is tall. They come to Earth's orbit to in 7.5 million kilometers (about 4.6 million miles). By comparison, when Mars and Earth are at their closest, they are about 53 million kilometers (about 33 million miles) apart. Potentially hazardous comets also grow unusually close to Earth.
Knowing the size, shape, mass, composition and form on these objects helps determine the best way to divert one, should it have an Earth-threatening path.
Meteors and Meteorites
While traveling through space, asteroids sometimes collide in the company of each other and shatter up into smaller fragments. Comets shed dust when they roam the solar system. These 'break ups' result inside numerous little particles and fragments, called meteoroids, which orbit the sun.
Most meteoroids are little and rocky. When one approaches Earth, it burns up when it goes through Earth's atmosphere. Thus a meteor, or shooting star, is formed.
Fireballs are larger meteoroids, roughly ranging inside size anywhere from a basketball to a Volkswagen. They also make highly impressive firmament displays when they shatter into fragments and burn up inside their passage through Earth's atmosphere.
Some meteoroids remain alive passage through Earth's air and hit the ground. These are called meteorites.

0 Comments
Posting Komentar